Heart stents, also known as coronary stents, and titanium alloy heart stents are important in continuously supporting arteries, solving stenosis problems, and ensuring smooth blood circulation. This medical device is mainly used in the treatment of acute coronary syndromes such as acute myocardial infarction and is a valuable tool for saving lives.
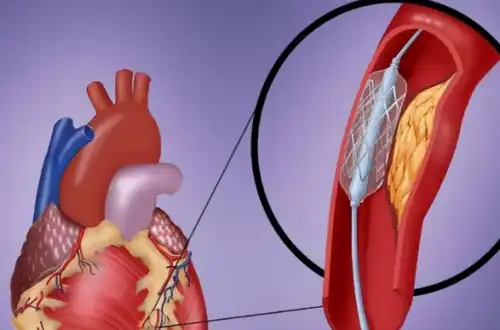
With the continuous advancement of medical technology, after repeated research and practice, the most commonly used material in heart stents is titanium alloy. Titanium alloy not only has high strength and corrosion resistance but also has good biocompatibility, which makes it an ideal choice for heart stents.
The manufacturing process of titanium alloy heart stents is very delicate. According to different treatment needs, the tube body of the stent will be precisely "carved". This stent supports the artery without causing excessive pressure on the surrounding tissues.
According to statistics, more than 10 million titanium alloy heart stent implantations have been completed worldwide. This number not only reflects the wide application of titanium alloy heart stents but also reflects its important position in the medical field.
During percutaneous coronary balloon angioplasty, the doctor will attach a pre-folded titanium alloy heart stent to the balloon. When the balloon is expanded, the stent will also open and fix the narrowed artery. This is the basic principle of intracoronary stenting.
At present, about 80% of coronary interventions in clinical practice will implant heart stents. These stents can not only effectively relieve patients' symptoms, but also significantly improve their quality of life. It is precisely because of the excellent application of titanium metal in heart stents that countless lives have been saved.











